A few years ago, I tried to engrave a wooden sign by hand. I had a vision—beautiful, intricate lettering burned into the wood. I bought a rotary tool, set up my workspace, and got to work. The result? A shaky, uneven mess that looked nothing like I had imagined.
That’s when I started researching other ways to engrave. And that’s when I discovered laser engraving.
If you’ve ever tried manual engraving or burning wood by hand, you know how frustrating it can be. Getting clean lines and perfect shapes is nearly impossible without the right tools. That’s why laser engraving is such a game-changer. It takes precision to a whole new level.
In this article, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about laser engravers—what they are, how they work, and why so many people use them for business, hobbies, and creative projects.
By the end, you’ll know exactly what a laser engraver does and whether it’s the right tool for you.
So let’s start!
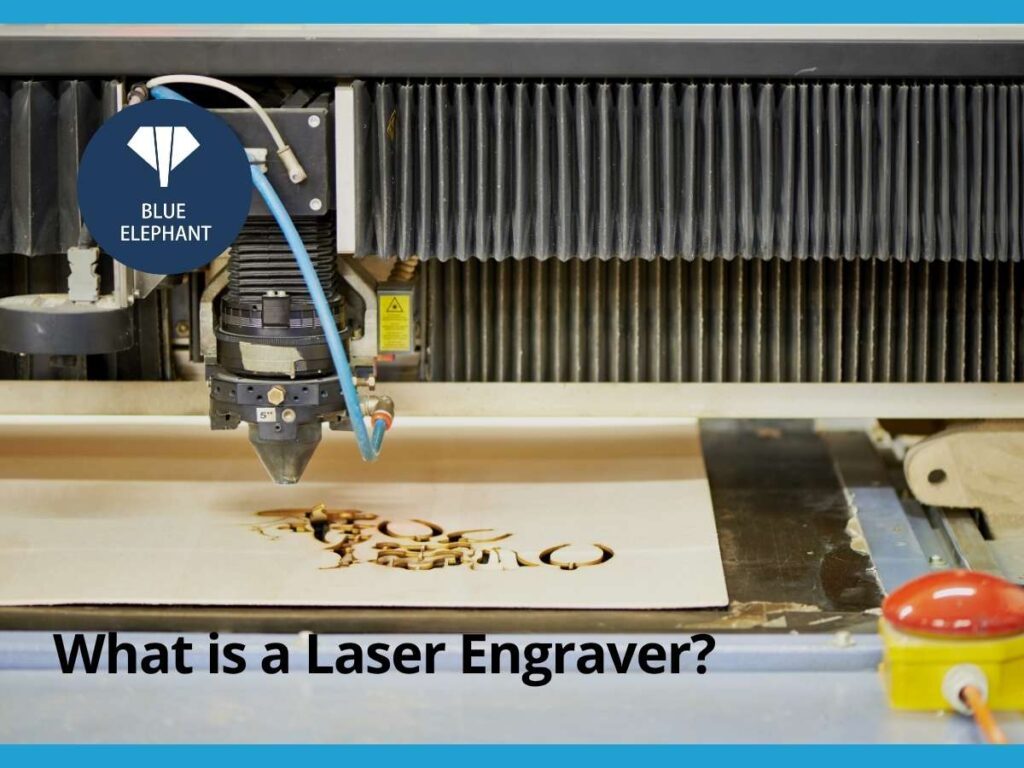
1. What is a Laser Engraver?
The first time I saw a laser engraving machine in action, I couldn’t believe my eyes. A thin, invisible beam cut through the surface of metal like it was nothing, leaving behind a crisp, permanent mark. No pressure, no mess—just pure precision. It made me wonder: Why isn’t every business using this?
If you’ve ever seen a perfectly engraved logo, serial number, or custom design and wondered how it was made, you’re in the right place.
Why Is Laser Engraving So Popular?
Industries and small businesses use laser engraving because it offers:
- Unmatched Precision: The laser beam can engrave intricate details, barcodes, serial numbers, and fine text without physical contact.
- Versatility: Works on various materials, including metals, wood, plastics, glass, and ceramics.
- Permanence: The engraved markings don’t fade, peel, or wear off, making them ideal for industrial labels, branding, and part identification.
- Speed and Efficiency: Automated laser engravers handle high production volumes while maintaining consistency.
- Minimal Maintenance: With no physical tools making contact, wear and tear are significantly reduced compared to traditional engraving methods.
For any business that deals with labeling, customization, or industrial part marking, laser engraving isn’t just an option—it’s a smarter way to work.
So are you looking for a laser engraver supplier that will meet your business needs? Consider Blue Elephant, we provide affordable spare parts and lifetime online support for ongoing assistance.
2. How Does a Laser Engraver Work?
Laser engraving works by using a concentrated laser beam to remove material from a surface. The heat from the laser interacts with the material, either vaporizing it or breaking it down layer by layer, leaving behind a permanent mark.
So how does that actually happen? Let’s break it down.
How a Laser Engraver Interacts with Material
A laser engraver operates on a simple principle: energy meets material. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Laser Generation: The engraver produces a high-energy laser beam using a light source like CO₂ or fiber optics.
- Focusing the Beam: Lenses and mirrors concentrate the laser into an ultra-fine point, directing it to the engraving area.
- Material Absorption: The material absorbs the laser’s energy, causing a reaction—either melting, burning, or vaporizing.
- Controlled Movement: The laser moves precisely across the surface, following the programmed design or pattern.
This process allows for incredible precision—even microscopic details can be engraved with perfect accuracy.
The Role of Heat and Vaporization
Unlike traditional cutting tools, laser engraving is completely contactless. That means no dull blades, no mechanical friction, and no wear on the machine. Instead, the laser relies on heat and vaporization to remove material.
- Vaporization: The laser’s heat turns solid material directly into gas, leaving a permanent mark with no debris.
- Melting and Oxidation: In some cases, materials like metal melt slightly under the laser and oxidize, creating dark, high-contrast engravings.
- Surface Disruption: For softer materials like wood or leather, the laser burns into the surface, creating a deep, textured engraving.
I once tested a laser engraver on stainless steel. The heat caused a chemical reaction on the surface, producing a dark, crisp engraving without cutting into the metal. That’s the beauty of laser engraving—it doesn’t weaken the material, but it alters it permanently.

3. Types of Laser Engraver
The first time I saw a laser engraver at work, I assumed all engravings were done the same way. But after working with different machines, it became clear—not all laser engravings are equal. Some are designed for detailed artwork, while others cut deep into metal for industrial use. The type of engraving depends on how the laser moves and how much material it removes.
So, which one is right for your business? Let’s go through the three main types.
Raster Engraving
Imagine printing an image on paper, but instead of ink, the design is burned onto a surface. That’s how raster engraving works. The laser moves back and forth, line by line, creating small dots that form an image.
- How It Works: The laser scans across the material, burning tiny dots to create shading and depth.
- Best For: Photographs, intricate designs, and logos on wood, acrylic, leather, and glass.
- Key Benefit: Captures fine details with smooth gradients and realistic shading.
A furniture company I worked with used raster engraving to etch floral designs onto wooden tabletops. The result? Stunning, high-contrast artwork that added value to their custom pieces. If your business involves custom branding, decorative engraving, or detailed graphics, this method is ideal.
Vector Engraving
For businesses that need clean, sharp lines rather than shading, vector engraving is the way to go. Instead of scanning back and forth, the laser follows a continuous path—much like a pen drawing on paper.
- How It Works: The laser traces the outline of the design, creating thin, precise lines.
- Best For: Serial numbers, barcodes, schematics, and text on metal, plastic, and coated materials.
- Key Benefit: Faster than raster engraving, perfect for high-volume production.
If you’re in manufacturing, product identification, or industrial labeling, vector engraving offers durability and efficiency.
Deep Engraving
Not all engravings sit on the surface. Some industries require markings that can withstand extreme conditions, from high temperatures to heavy wear. Deep engraving removes more material than other methods, leaving behind markings that last a lifetime.
- How It Works: The laser makes multiple passes over the material, gradually removing deeper layers.
- Best For: Aerospace, automotive, and military parts requiring long-lasting identification.
- Key Benefit: Resistant to wear, corrosion, and environmental damage.
One of the toughest engraving jobs I’ve seen was on turbine blades used in aircraft engines. The markings had to survive extreme heat and stress. Deep engraving made them permanent, even after years of use. If you work in high-stakes industries where identification is critical, this is the best option.

4. Features to Look for in a Laser Engraver Machine
Choosing the right laser engraver isn’t just about price or brand—it’s about getting the right tool for the job. I’ve seen businesses struggle with machines that were either too weak for their materials or too slow for production demands. The right engraver can save time, improve precision, and handle the workload you need.
So, what should you look for? Let’s break it down.
Power & Wattage
Laser power is measured in watts, and it directly impacts engraving depth and material compatibility.
- Low Power (10W-40W): Best for engraving on paper, leather, acrylic, and thin wood. Ideal for small crafts and hobbyists.
- Mid Power (50W-100W): Suitable for deeper engravings on wood, plastics, and coated metals. Great for small businesses and workshops.
- High Power (100W-500W and above): Designed for industrial engraving on stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. Necessary for deep engraving and cutting thicker materials.
Always consider the materials you’ll be engraving. A lower-wattage CO₂ laser may work for wood, but metals require fiber lasers with higher wattage.
Engraving Speed & Precision
A faster machine sounds great, but speed can come at the cost of detail. Finding the right balance between engraving speed and precision is key.
- DPI (Dots Per Inch): Higher DPI means finer details but slower speeds. Lower DPI engraves faster but sacrifices detail.
- Speed Settings: Adjusting power and speed settings ensures clean engravings without burning or overcutting.
- Servo vs. Stepper Motors: Servo motors provide smoother, high-speed movements for better accuracy in mass production. Stepper motors are cheaper but may cause slight misalignment in long engravings.
Software Compatibility & Connectivity
A laser engraver is only as good as the software that controls it. Some machines only work with specific programs, while others offer flexibility.
- Best Software Options:
- LightBurn: User-friendly, feature-rich, works with most lasers.
- CorelDRAW & AutoCAD: Best for detailed vector designs and industrial applications.
- EZCAD: Primarily used for fiber laser engraving on metal.
- Connectivity Options:
- USB: Standard, reliable, but requires a dedicated PC connection.
- Wi-Fi & Cloud-Based: Allows wireless control and remote job management.
- Ethernet: Stable for networked production environments.
A business partner of mine bought a laser engraver that only worked with outdated software. They spent hours converting files instead of focusing on production. Make sure your engraver supports the design software you already use.
5. Common Applications of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is everywhere—you just might not realize it. From serial numbers on industrial parts to custom logos on wood signs, this technology plays a major role in both large-scale manufacturing and small businesses.
I remember talking to a machine dealer who once dismissed laser engraving as “just for arts and crafts.” That was until he saw it in action at a factory, marking hundreds of metal parts with precise, permanent serial numbers in minutes.
So, where is laser engraving used the most? Let’s take a look.
Industrial & Business Uses
- Manufacturing & Metal Engraving: Factories use laser engraving to mark serial numbers and part IDs on metal components, ensuring traceability and compliance with industry regulations. Machine dealers and resellers benefit by offering precision-marked parts that meet quality standards.
- Advertising & Signage: Businesses use laser engraving to create high-end promotional products, branded merchandise, and durable signage. Marketing firms and resellers can offer engraved items as premium custom branding solutions.
- Furniture & Interior Design: Laser engraving adds intricate patterns to wood, glass, and acrylic for furniture and décor. Interior designers and manufacturers use it to enhance product aesthetics and create unique, customized pieces. If you are in this industry and looking for durable laser engraver machines, choose Blue Elephant. We offer remote troubleshooting, on-site visits, and detailed user guides for seamless operations.
Small Business & Personal Projects
- Custom Gifts & Crafting: Engraving allows businesses to create personalized gifts, from engraved jewelry to custom leather goods. Small business owners and online sellers use it to attract customers looking for unique, high-quality products.
- Mold Design & Production: Mold manufacturers use laser engraving to add fine details, part numbers, and branding to molds, improving durability and production accuracy. Tooling companies and industrial resellers rely on this process for high-precision applications.
6. Safety Guidelines When Using a Laser Engraver
Laser engraving is powerful, precise, and efficient—but it also comes with risks. So, how do you stay safe? Let’s go over the key guidelines.
Protective Equipment & Safe Work Environment
Laser engraving generates intense heat, bright light, and airborne particles, making protective gear and a controlled workspace essential.
- Laser Safety Glasses: Protects against harmful reflections from high-powered lasers. Make sure the glasses are rated for your laser’s wavelength (CO₂, fiber, or diode).
- Ventilation & Exhaust Systems: Removes smoke, fumes, and airborne particles from materials like acrylic and coated metals, preventing toxic exposure.
- Fire Safety: Laser engraving can ignite flammable materials. Keep paper, fabrics, and other combustibles away from the machine. Always have a fire extinguisher within reach.
A machine repairer once told me about a fire that started because an operator left their engraver unattended while cutting wood. Even small mistakes can lead to major safety hazards. Never leave a running laser unattended.
Regulatory & Compliance Considerations
Using a laser engraver in a business setting means following safety regulations to protect both employees and customers.
- CE (Conformité Européenne) & FDA Certification: Ensures the machine has proper safety enclosures, emergency stop functions, and laser shielding. If you’re buying a commercial engraver, check that it meets these standards.
- Workplace Ventilation & Exhaust Compliance: In industrial settings, improper ventilation can lead to fines or safety violations. Always confirm that your exhaust system meets occupational safety regulations for air quality.
7. Tips on How to Choose the Best Laser Engraver Machine
Choosing the right laser engraver isn’t just about price—it’s about getting the right tool for your specific needs. I once worked with a manufacturer who bought a high-powered fiber laser to engrave wood, only to realize later that a CO₂ laser was the better choice. Avoiding mistakes like this can save both time and money.
Tip #1 Consider Power & Wattage
Wattage affects engraving depth, speed, and material compatibility. Low-power machines (10W-40W) work well for thin wood, leather, and plastics but are too weak for industrial applications. Mid-range machines (50W-100W) can handle deeper engravings on wood, coated metals, and some plastics.
High-powered lasers (100W-500W) are required for deep metal engraving and industrial marking. One business I consulted bought a low-wattage CO₂ laser for stainless steel, only to realize too late that they needed a fiber laser to get clean results.
Tip #2 Choose the Right Work Area Size
The engraving bed size determines the maximum piece you can engrave in one pass. Small work areas (8”x12”) are fine for small products like keychains and plaques. Medium sizes (12”x24” to 24”x36”) allow for larger signs and branding projects. Large-scale engravers (36”x48” and above) are essential for bulk production and furniture engraving.
Tip #3 Pay Attention to Engraving Speed & Precision
A machine’s speed and resolution settings impact both efficiency and quality. Higher DPI settings produce more detailed engravings but slow down the process, while lower DPI speeds up production at the cost of fine details. Servo motors provide smoother, faster motion for industrial applications, while stepper motors are slower but more affordable.
Tip #4 Make Sure It’s Compatible with Your Software
Not all laser engravers work with the same design software. LightBurn is widely used for its user-friendly interface and compatibility with both CO₂ and fiber lasers. CorelDRAW and AutoCAD are preferred for industrial applications that require detailed vector engraving. EZCAD is often used with fiber lasers for metal marking.
Conclusion
We’ve covered everything—how laser engraving works, the different types of machines, safety precautions, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
Whether you’re in manufacturing, advertising, or small-scale crafting, the right laser engraver can change the way you work.
Choose wisely, invest in the right engraver, and start creating high-quality, permanent designs.
At Blue Elephant, we specialize in providing high-quality CNC laser engravers built for precision and efficiency.
Contact us today, and let’s find the perfect machine for your business!
Explore More Helpful Resources
For more in-depth knowledge, take a look at these recommended reads. We think you’ll find them useful:
Comparisons & Maintenance
- Top 10 Laser Cutters
- Buying A Second Hand Laser Engraver: What You Need To Know?
- 9 Maintenance Checks for Your Laser Cutting Machine
- Is a Used Laser Cutter Worth It? What You Need to Know
Technology & Alternatives
- CNC vs Laser Cutter: Key Differences
- Plasma Cutter vs Laser Cutter: A Complete Comparison
- Die Cut vs Laser Cut: A Quick Comparison Guide
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.