I remember walking through a factory, watching workers mark thousands of parts per hour. But what caught my attention wasn’t the speed, it was the precision. Every mark was crisp, clean, and permanent. No fading. No smudging. No errors.
I asked the owner how they kept their markings so sharp. His answer? Laser marking. He explained how it worked, why they switched from ink-based marking, and how it saved them money while improving quality.
That conversation changed how I saw industrial marking forever.
Now, I want to share what I’ve learned with you. If you’re wondering what a laser marker is, how it works, and whether it’s worth investing in, this guide will give you clear answers.
So let’s get started!
1. What Is a Laser Marker?
The first time I saw a laser marker in action, I was amazed. A beam of light touched metal, and within seconds, a clear, permanent mark appeared. No ink, no pressure just precision. It felt like magic. But there’s no magic here, just smart technology.
A laser marker is a machine that uses a concentrated beam of light to create marks on a surface. These marks can be logos, barcodes, serial numbers, or even decorative designs. Unlike printing or engraving, laser marking is fast, accurate, and permanent.
The process doesn’t wear down the material. There’s no need for ink or chemicals. The laser simply changes the surface—either by heating, oxidizing, or engraving a shallow mark.
Why Is Laser Marking Important?
If you’ve ever used a product with a serial number or seen a metal tag with engraved letters, you’ve seen laser marking at work. It’s used everywhere.
Here’s why it matters:
- Permanent Marks: Laser markings don’t fade, smudge, or wash off. They last as long as the material itself.
- No Contact, No Wear: Unlike stamping or printing, a laser doesn’t touch the material. That means no tool wear and no damage to delicate surfaces.
- Works on Many Materials: Metal, plastic, wood, glass, leather—you name it, and there’s a laser marker that can handle it.
- Fast and Precise: It can mark thousands of parts per hour with perfect accuracy.
For businesses, laser marking isn’t just a tool—it’s an investment. It saves time, reduces waste, and makes products look professional. Whether you’re a manufacturer, an artist, or a repair technician, laser marking can be a game-changer.
And the best part? Once you set it up, it just works. With high-precision machines from Blue Elephant, you get reliable performance, durable markings, and seamless operation—so you can focus on growing your business instead of worrying about production delays.
2. How Does a Laser Marker Work?
A laser marker might look simple from the outside, but inside, it’s doing some impressive work. Instead of using ink, a blade, or a stamping press, it focuses a powerful beam of light to create a precise, permanent mark. No physical contact. No moving parts grinding against the surface. Just light and precision.
This is why laser marking is so reliable. There’s no wear and tear, no need for refills, and the results are always consistent. But how does it actually work?
Basics of How It Works
A laser marker has a few key parts that work together:
- Laser Source: This produces the laser beam. Different types (fiber, CO₂, UV) are used for different materials.
- Scanning System: Mirrors move the beam across the surface, guiding the mark.
- Controller & Software: This tells the laser what to do, adjusting speed, depth, and design.
- Work Surface: The platform where the object is placed for marking.
The Laser Marking Process
- Design Loaded: The operator creates or uploads a design into the software.
- Material Positioned: The object is placed on the work surface.
- Laser Engages: The machine directs the laser beam to the exact points needed.
- Marking Happens: The laser changes the surface by heating, oxidizing, or slightly engraving it.
- Final Product: A clean, permanent mark remains.
It all happens in seconds. No messy ink, no physical contact, no waiting for anything to dry.
Different Ways a Laser Can Mark
A laser marker isn’t a one-size-fits-all tool. Depending on the material and design, it can mark in different ways:
- Annealing: Creates a dark mark on metals by heating the surface.
- Foaming: Used on plastics, creating a raised, lighter-colored mark.
- Color Change: Alters the surface of plastic without burning or melting it.
- Engraving: Removes material for a deeper, permanent mark.
This is why laser markers are used everywhere. They’re fast, precise, and versatile. Whether you need a logo on a metal tool or a serial number on a circuit board, a laser marker gets the job done with zero waste and no extra materials.
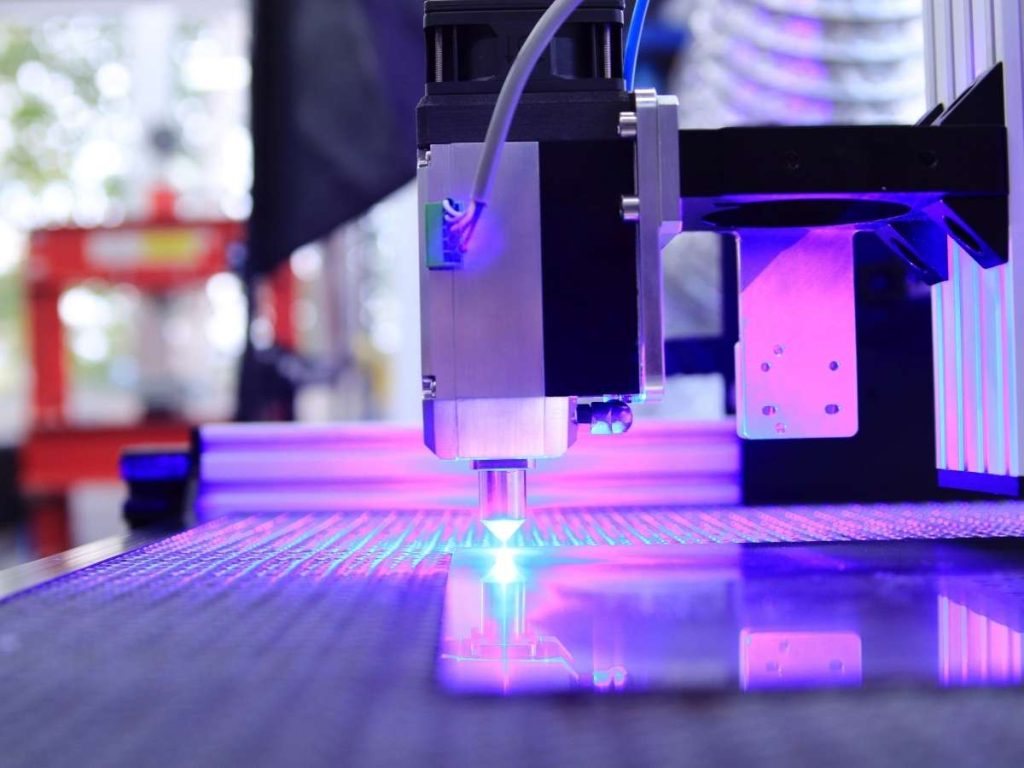
3. Key Benefits of Using a Laser Marker
Unlike traditional methods, a laser marker doesn’t use ink, chemicals, or pressure. It works with pure light, creating marks that last without wearing down tools or materials. That’s why industries rely on it for fast, durable, and precise marking. Let’s break down the key benefits.
No Contact, No Wear and Tear
I’ve seen what happens to engraving tools after a few months of heavy use. Bits get dull. Blades chip. Machines need constant maintenance. That’s the problem with physical marking methods—they wear down over time.
Laser marking is different. It’s a non-contact process, meaning:
- The laser never touches the material, preventing surface damage.
- No cutting or grinding, so there’s no dust or debris.
- No need to replace worn-out tools, reducing maintenance costs.
This makes it ideal for businesses that need precision without downtime.
Permanent and High-Precision Marking
I once saw a batch of metal parts rejected because the printed barcodes had faded. That’s an expensive mistake. With laser marking, that wouldn’t have happened.
Laser marking creates high-contrast, long-lasting marks that resist:
- Fading and smudging (unlike ink or stickers).
- Heat and chemical exposure (great for medical and industrial use).
- Scratches and wear (ideal for tools, machines, and electronics).
It’s also incredibly precise. Whether you need tiny serial numbers or intricate logos, laser markers deliver clean, detailed results every time.
No Ink, No Chemicals Just Light
Many marking methods require ink, acids, or solvents, which add costs and maintenance. Laser marking eliminates those extra expenses.
With laser marking, you:
- Save money with no ink cartridges or refills needed.
- Reduce waste with no leftover chemicals or consumables.
- Improve safety with no toxic fumes or handling hazards.
For businesses looking to cut costs and stay environmentally friendly, laser marking is a great alternative.
Fast and Efficient for High-Volume Production
Speed matters, especially in manufacturing. A slow marking process can hold up production and increase labor costs.
Laser markers are built for efficiency:
- Fast processing times marks are created in seconds.
- Automated operation can integrate with production lines.
- Minimal downtime means no need to stop for refills or maintenance.
That’s why industries like automotive, packaging, and industrial manufacturing depend on laser markers to keep production moving.
Works on a Wide Range of Materials
One of the biggest advantages of laser marking is its versatility. It works on a variety of materials, including:
- Metals (steel, aluminum, brass).
- Plastics (acrylic, ABS, polycarbonate).
- Wood (MDF, plywood, hardwood).
- Glass (bottles, awards, display pieces).
- Leather, textiles, ceramics, and more.
This flexibility makes laser marking useful for everything from industrial parts to custom-engraved products.
Laser marking is a durable, cost-effective, and efficient solution for businesses. It eliminates the need for consumables, reduces maintenance, and delivers consistent, high-quality results on a wide range of materials.
For companies that need permanent, high-precision marking without extra costs or downtime, laser marking is one of the best investments they can make.
4. Types of Laser Markers and Their Applications
Not all laser markers work the same way. Some are built for fast, deep marking on metal, while others are better for delicate materials like glass or plastic. The right laser depends on the material, industry, and level of precision needed.
Here’s a breakdown of the four main types and where they’re used:
Fiber Laser Markers: Best for Metal
A fiber laser marker is the go-to choice for marking metal. It produces high-contrast, long-lasting marks without damaging the material. This makes it ideal for industries that require durable, permanent identification.
Common Uses:
- Aerospace & Automotive: Serial numbers and barcodes on metal parts.
- Medical Industry: Marking surgical tools and implants.
- Electronics: Circuit board labeling and micro-marking.
Key Benefits:
- Fast and efficient for high-volume production.
- Works on tough materials like steel, aluminum, and titanium.
- Marks don’t fade, even under heat or friction.
A shop owner once told me how they switched from ink printing to fiber laser marking for metal tools. The ink smudged too easily, but the laser marks never faded—even after months of wear.
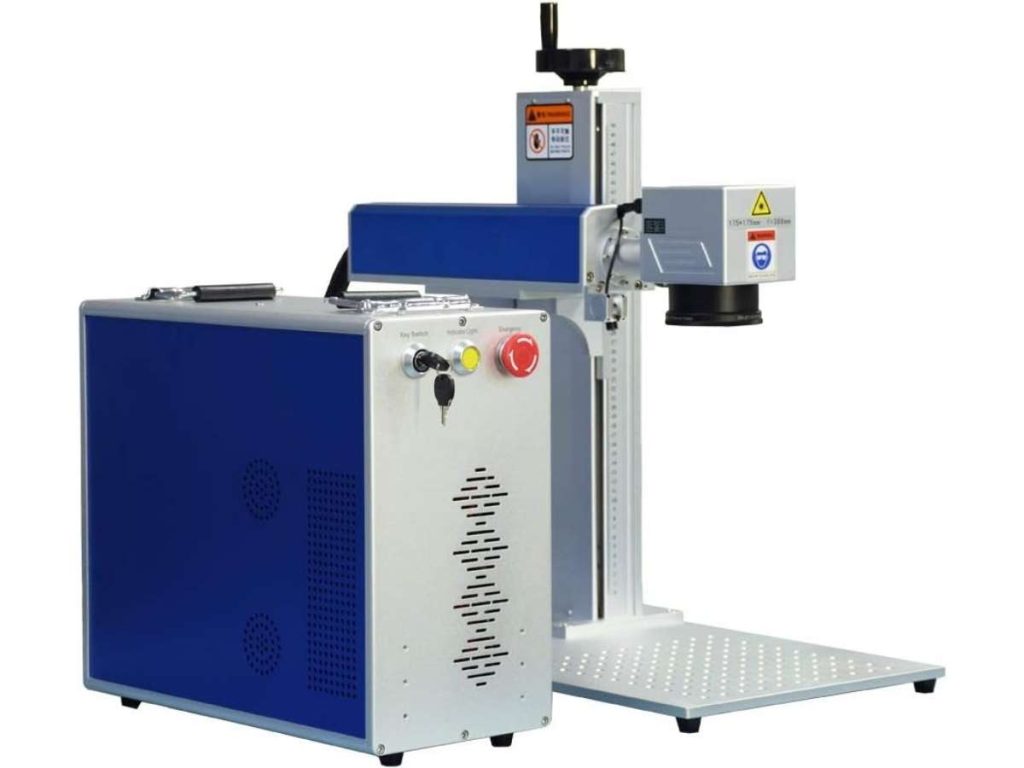

CO₂ Laser Markers: Best for Non-Metals
CO₂ lasers are a favorite for woodworking shops, custom engravers, and packaging companies. Instead of cutting into metal, they work best on organic and synthetic materials like wood, acrylic, leather, and glass.
Common Uses:
- Signage & Packaging: Logos on wood, paper, and plastic packaging.
- Crafts & Personalization: Custom engravings on leather, glass, and fabric.
- Product Labeling: Serial numbers on plastic containers and bottles.
Key Benefits:
- Perfect for smooth, detailed engraving on non-metals.
- No risk of burning or warping delicate materials.
- Widely used in retail, advertising, and customization.
A friend who runs a laser engraving business once showed me a leather wallet she customized with a CO₂ laser. The details were clean, and unlike ink, the mark wouldn’t rub off over time.
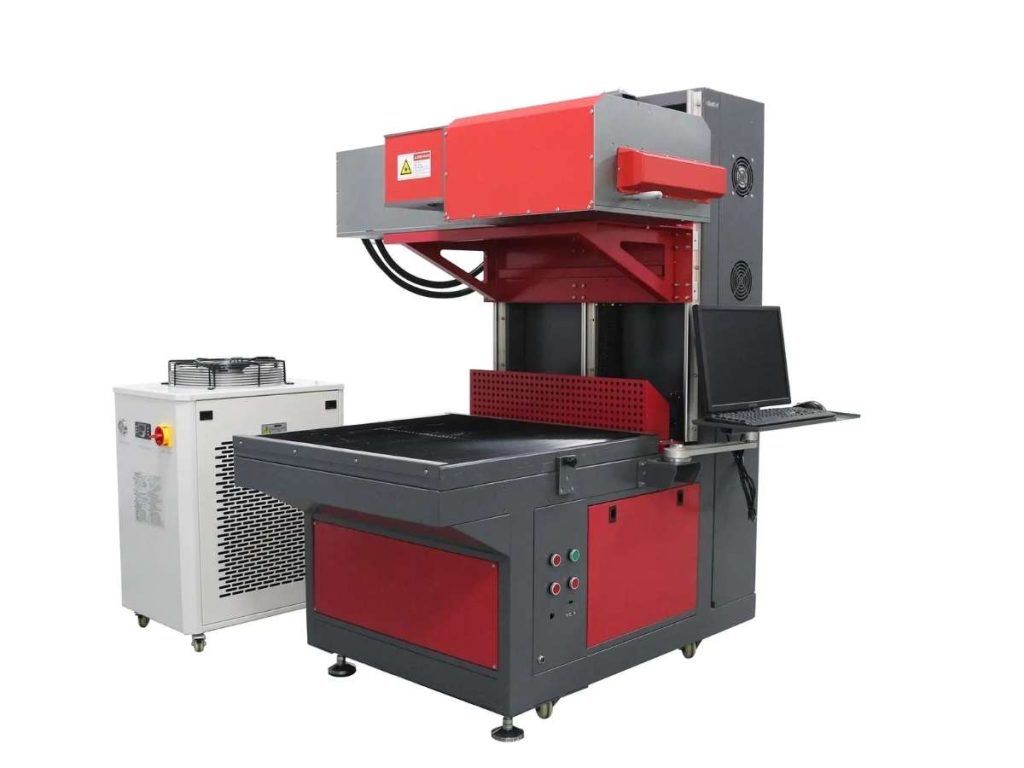

UV Laser Markers: High Precision for Delicate Materials
UV lasers are the specialists of the laser marking world. They work at a shorter wavelength, which means they generate less heat. This makes them perfect for delicate materials where heat damage is a risk.
Common Uses:
- Electronics: Marking circuit boards, connectors, and plastic buttons.
- Medical Devices: Engraving on syringes, test tubes, and small tools.
- Cosmetic & Pharmaceutical Industry: Expiration dates and batch numbers on bottles.
Key Benefits:
- Minimal heat damage—safe for sensitive materials.
- Works on both plastics and metals with precision.
- Creates ultra-fine, high-contrast markings.
A manufacturer once told me they had issues with barcodes fading on plastic medical devices. When they switched to UV laser marking, the issue disappeared. The marks were crisp, readable, and unaffected by sterilization.
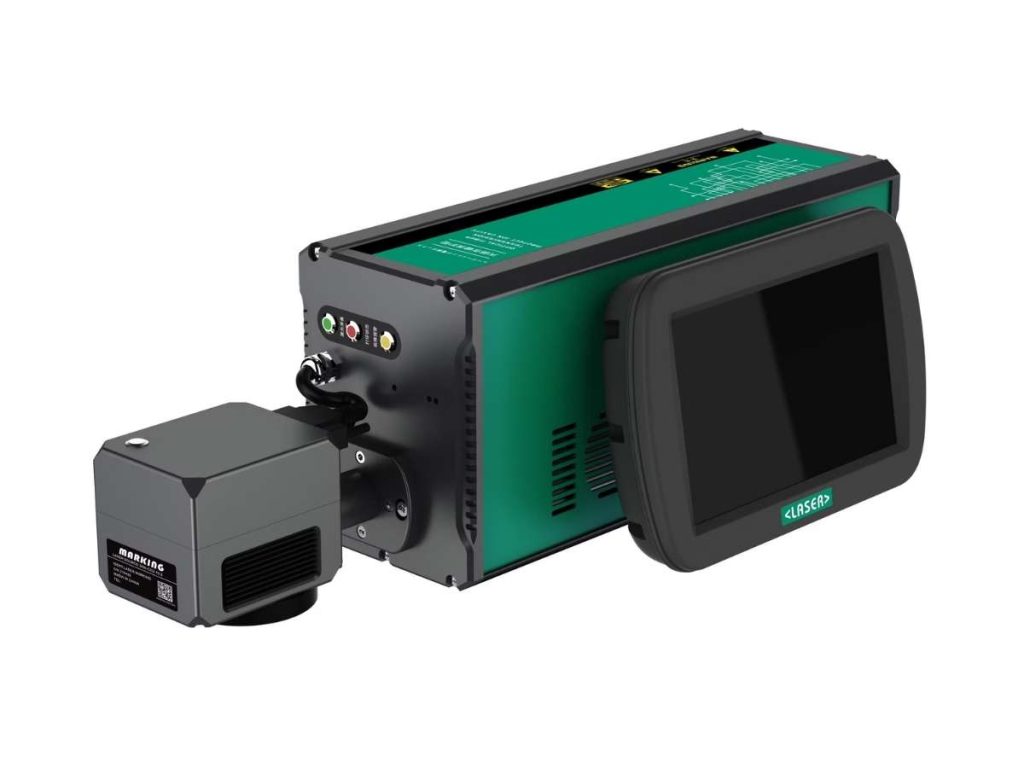

Green Laser Markers: Best for Specialized Materials
Green lasers are less common but extremely useful. They operate at a specific wavelength that makes them ideal for fragile materials like silicon, ceramics, and thin plastics.
Common Uses:
- Microelectronics: Marking silicon wafers and delicate semiconductors.
- Medical Applications: Labeling glass vials and precise surgical tools.
- Jewelry & High-End Engraving: Engraving fine details on sensitive materials.
Key Benefits:
- Perfect for materials that crack or burn under traditional lasers.
- Ultra-precise, even at microscopic levels.
- Used in high-tech industries where precision is key.
One engineer told me how they struggled to mark silicon components without damaging them. A fiber laser was too strong, but the green laser left a flawless mark with zero distortion.
Choosing the right laser depends on what material you’re working with and how durable the mark needs to be. Whether you’re engraving a barcode on steel or personalizing a leather wallet, there’s a laser marker built for the job.
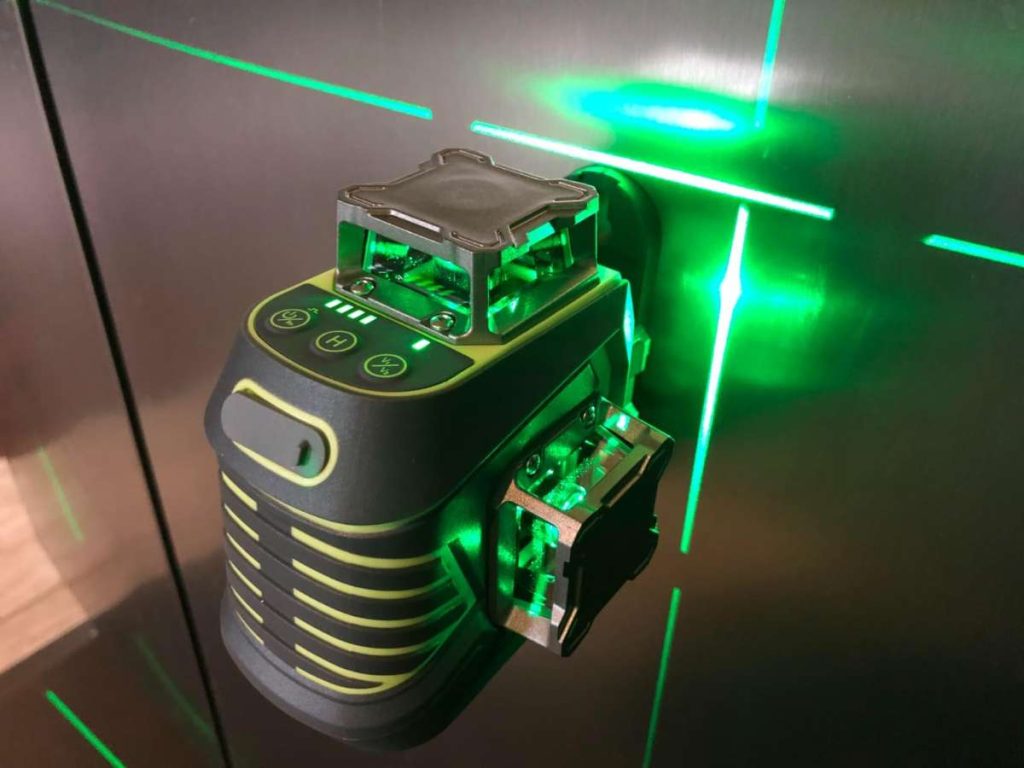

5. Industries That Benefit from Laser Marking
Laser marking is everywhere. You just might not notice it. Look at the back of your phone, the bottom of a soda can, or even a barcode on a medical device. That mark was likely made by a laser.
Why? Because laser marking is fast, precise, and permanent. It doesn’t wear off like ink or stickers. It doesn’t damage delicate parts like stamping or engraving. That’s why so many industries rely on it.
Let’s look at some of the biggest industries that benefit from laser marking.
Manufacturing & Industrial Applications
Factories run on efficiency. Every part needs to be labeled for tracking, inventory, and quality control.
Laser markers help manufacturers by creating:
- Serial numbers for product identification.
- Barcodes and QR codes for inventory tracking.
- Logos and branding for product authentication.
Since laser marks are permanent and resistant to fading, they help companies avoid counterfeiting and maintain quality control.
Automotive & Aerospace
When it comes to cars and airplanes, safety and durability are everything. Parts must be traceable and withstand heat, friction, and chemicals.
Laser marking ensures:
- Identification codes on engine and transmission parts.
- VIN numbers and compliance labels for regulations.
- Durable markings that survive extreme environments.
An aerospace engineer once said that laser-marked parts can handle more stress than other labeled components. That’s why it’s a standard in aircraft manufacturing.
Electronics & Semiconductors
Electronics are getting smaller and more complex. Traditional labeling methods don’t work on microchips and circuit boards. Laser marking does.
It’s used for:
- Component identification on tiny PCBs.
- Branding on casings without damaging the material.
- Traceability codes for recalls and quality checks.
Since lasers work without contact, there’s no risk of damaging delicate micro-components.
Medical & Pharmaceuticals
Medical devices must be safe, traceable, and FDA-compliant. Laser marking makes that easy.
It’s used for:
- Marking surgical tools and implants with serial numbers.
- Expiration dates and batch numbers on pharmaceutical packaging.
- Sterilization-resistant labeling for medical equipment.
A hospital supplier once told me how laser marking helps track surgical tools—reducing lost equipment and ensuring proper sterilization.
Jewelry & Customization
Laser marking isn’t just for industry. It’s also used for personalized engravings on fine jewelry.
Popular applications include:
- Engraving names and initials on rings and bracelets.
- Custom designs on gold, silver, and platinum.
- Marking serial numbers on high-value pieces to prevent counterfeiting.
The high precision of laser marking allows for detailed, intricate designs that traditional engraving methods can’t achieve.
Advertising & Signage
Laser marking is also big in branding and marketing. Businesses use it to make high-quality promotional products and custom signage.
- Company logos on metal pens, keychains, and corporate gifts.
- Indoor and outdoor signs with crisp, detailed lettering.
- High-end branding on glass, wood, or acrylic surfaces.
A print shop owner told me they stopped using traditional printing for promotional products. Laser marking lasts longer and looks more professional.
No matter the industry, laser marking saves time, reduces waste, and delivers high-quality results—making it a trusted solution for businesses worldwide.
6. Common Laser Marking Problems and How to Solve Them
Laser marking is precise, fast, and reliable. But like any machine, things don’t always go smoothly. Sometimes the marks come out too light, other times there’s unwanted burning. And let’s not forget software issues that can throw off an entire job.
If you’ve run into problems with laser marking, don’t worry. Most issues have simple fixes. Here are some of the most common problems—and how to solve them.
Faded or Weak Marking
A laser mark should be crisp and easy to read. But sometimes, it looks faint or uneven.
Possible Causes & Fixes:
- Low Laser Power: Increase the power setting to make a deeper mark.
- Incorrect Frequency: Adjust the pulse frequency to match the material.
- Wrong Laser Type: Fiber lasers work best on metal, while CO₂ lasers are better for wood and plastic.
If a mark looks too light, start by adjusting the power settings in small increments. Testing on a scrap piece can help you find the right balance.
Burn Marks on Materials
Some materials, like plastic or wood, are sensitive to heat. Too much power and you’ll end up with burn marks or melted edges.
How to Prevent Burn Marks:
- Lower the Power Settings: Too much energy can scorch the surface.
- Shorten the Pulse Duration: A faster pulse reduces heat buildup.
- Use a UV or Green Laser: These lasers create cleaner marks on heat-sensitive materials.
If burns are a problem, fine-tune the settings and test on a sample first. A cooling system or air assist can also help reduce overheating.
Software or Design Errors
Sometimes, the issue isn’t with the laser—it’s with the design. If a mark comes out distorted, missing parts, or improperly placed, software settings may be the culprit.
Ways to Fix Software Issues:
- Check File Compatibility: Some laser machines require specific file formats like SVG or DXF.
- Use Vector-Based Designs: Raster images can lose detail, while vector files provide clean, sharp lines.
- Align Your Workpiece Properly: Misalignment in the software can lead to incorrect positioning.
Keeping software up to date and using high-quality design files can help avoid these problems.
Machine Maintenance Tips
A well-maintained laser marker runs smoothly and produces consistent, high-quality results. Regular maintenance helps prevent common issues before they start.
Best Maintenance Practices:
- Clean the Lens and Mirrors Regularly: Dust and debris can weaken the laser beam.
- Calibrate the Machine: Regular calibration ensures accuracy and alignment.
- Check for Software Updates: Bug fixes and performance improvements can prevent unexpected errors.
A simple cleaning routine and scheduled maintenance checks will keep your laser running like new.
Laser marking problems can be frustrating, but most have straightforward solutions. Whether it’s adjusting settings, switching materials, or maintaining your machine, small tweaks can make a big difference.
By keeping power levels optimized, software updated, and equipment well-maintained, you’ll get consistent, high-quality marks every time.
7. Choosing the Right Laser Marker for Your Business
Not all laser markers are the same. The right one depends on what you’re marking, how fast you need it, and your budget. A small shop engraving custom gifts has different needs than a factory marking thousands of metal parts daily.
So how do you choose? Here are the key factors to consider.
Material Compatibility
The first step is knowing what materials you’ll be marking. Different lasers work best for different surfaces.
- Fiber Lasers: Best for metal (steel, aluminum, brass).
- CO₂ Lasers: Great for wood, acrylic, leather, and glass.
- UV Lasers: Perfect for plastics and delicate materials.
- Green Lasers: Designed for sensitive materials like silicon and ceramics.
If you work with multiple materials, consider a machine that supports different wavelengths or attachments.
Speed & Production Needs
Do you need quick, high-volume marking or detailed, slower engraving?
- High-Speed Fiber Lasers: Ideal for factories and mass production.
- Co₂ and Uv Lasers: Better for small businesses and intricate designs.
If you’re running batch production, speed is key. If you’re engraving fine details, precision matters more than speed.
Software & Ease of Use
Some laser markers are plug-and-play, while others require advanced setup.
- Look for user-friendly software if you’re a beginner.
- Check compatibility with industry-standard programs (AutoCAD, CorelDRAW, LightBurn).
- Automation features can save time in high-production settings.
A well-designed interface and workflow can make or break productivity.
Budget & Maintenance Costs
Laser markers range from affordable desktop models to high-end industrial machines. Consider both:
- Initial Investment: Higher-quality machines cost more upfront but last longer.
- Maintenance: Some machines require lens cleaning and part replacements.
- Operating Costs: No ink or consumables, but power and cooling costs apply.
Investing in a trusted brand like Blue Elephant ensures low maintenance and long-term reliability.
Space & Power Requirements
Think about where your machine will go and what power it needs.
- Desktop Lasers: Compact, great for small businesses and workshops.
- Industrial-Grade Machines: Require dedicated space and ventilation.
- Power Supply: Some need standard outlets, others require higher voltage.
If space is limited, a compact CO₂ or UV laser might be the best fit. If you’re in manufacturing, a large fiber laser with an enclosure is a better investment.
Whether you’re running a large-scale operation or a small business, investing in the right machine will save you time, money, and frustration in the long run.
Conclusion
Every business wants faster production, lower costs, and better quality. Laser marking gives you all three.
But only if you choose the right machine.
Think about what you need. Metal marking? High speed? Budget-friendly options? The answers are here.
Don’t let indecision slow you down. Start looking for the perfect laser marker now—the one that fits your business like a glove.
So, what’s your next step? If you have questions, we’re here to help. Contact us today!
Check Out These Additional Resources
Want to see more products? We’ve got plenty of options that might just be the perfect fit for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.












