I once burned through a full sheet of stainless—wrong machine, wrong settings, wrong choice.
It was a plasma cutter. What I really needed was a laser.
That mistake cost me more than just metal. It taught me the hard way that not all cutting methods are created equal.
It took me years to gain the right knowledge, and I’ve seen what happens when people pick the wrong tool. Some waste money on features they’ll never use. Others end up frustrated by slow speeds or poor-quality cuts.
That’s why I put this guide together. It breaks down the key differences between plasma and laser cutters in a way that actually makes sense.
By the end, you’ll know exactly which one fits your needs—so you can invest with confidence.
Let’s get started!
1. How Plasma Cutter and Laser Cutter Works?
The first time I used a plasma cutter. Sparks flew, the metal hissed, and I felt like I had unlocked a new level of fabrication. But my excitement quickly faded when I realized my cuts weren’t as clean as I wanted. That’s when I started wondering—was a laser cutter the better choice?
If you’re here, you might be asking the same thing. Which cutter is right for your work? Let’s break it down in a way that actually makes sense.
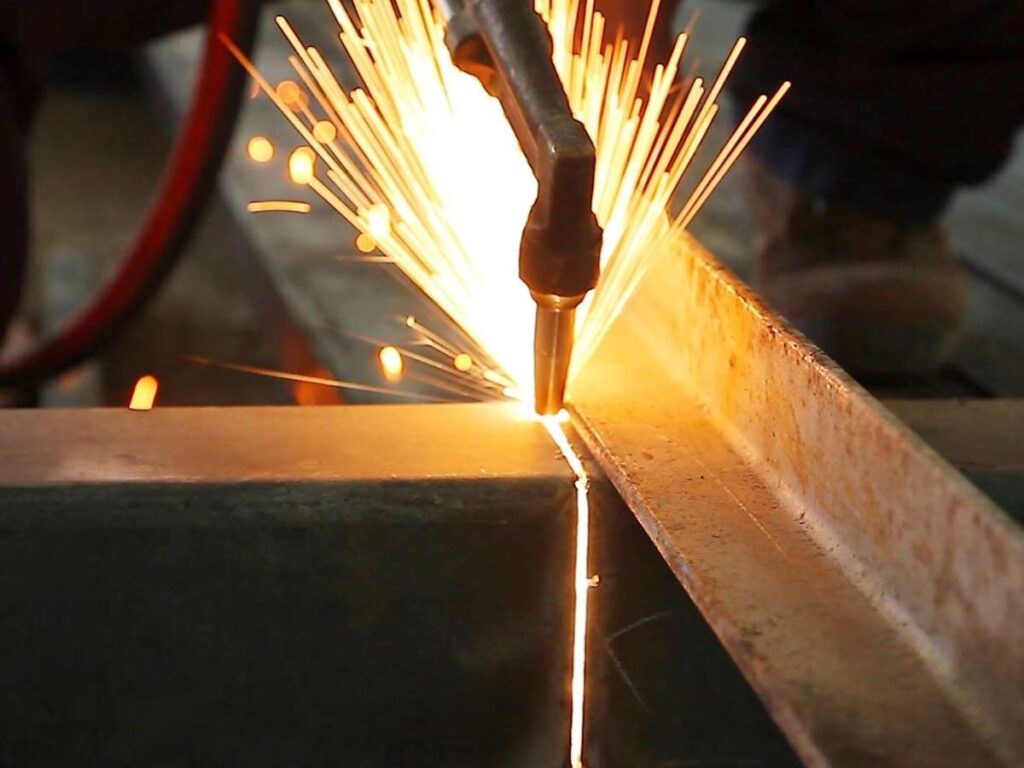
How Plasma Cutting Works
Plasma cutting is a go-to for fast, powerful cuts on thick metals. It’s been around for decades and is a favorite in repair shops, fabrication plants, and industrial sites. But how does it work?
A plasma cutter generates an electric arc that passes through a gas, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or argon, turning it into a superheated plasma stream that melts metal on contact. The ionized gas becomes conductive, allowing the plasma to cut through even thick materials with precision. As the plasma stream cuts, a high-velocity flow of compressed air or gas blows away the molten metal, leaving a visible separation in the material.
Why Businesses Use Plasma Cutting
I’ve seen shops rely on plasma cutting for one main reason—it just gets the job done fast. It’s also:
- Great For Thick Metal: Works on steel, aluminum, and stainless steel several inches thick.
- More Budget-Friendly: Plasma cutters cost less than laser machines and require less maintenance.
- Forgiving On Dirty Metal: Unlike lasers, plasma doesn’t need a spotless surface. Rust, paint, and dirt? Not a problem.
How Laser Cutting Works
Laser cutting is about precision. If you’ve ever seen perfectly clean, sharp metal edges, chances are they were cut with a laser. But is it the right tool for you?
A laser cutter uses a highly concentrated beam of light to melt, burn, or vaporize material with extreme accuracy. The laser beam is directed through a lens system that focuses its energy on a small point, generating intense heat to create a clean cut. An assist gas, such as oxygen or nitrogen, removes debris from the cutting area and prevents oxidation, ensuring a smooth finish with minimal distortion.
Why Businesses Use Laser Cutting
I’ll be honest—laser cutting blew my mind the first time I used it. The edges were so clean, I didn’t have to do any post-processing. Here’s why many companies love it:
- High Precision: Cuts as thin as 0.1 mm, meaning little to no finishing work needed.
- Minimal Heat Distortion: Less risk of warping compared to plasma cutting.
- Works On More Materials: Can cut thin to medium-thickness metals as well as acrylic, wood, and plastics.
- Automation-Ready: A favorite in mass production, aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
2. Performance Comparison: Which One is Better?
Choosing between a plasma cutter and a laser cutter isn’t just about price—it’s about performance. If speed and precision matter to your work, which one should you go with?
I’ve worked with both, and I can tell you—each has its strengths. But if you pick the wrong one, you might end up wasting time, money, and materials.
Let’s compare cutting speed and precision side by side.
Cutting Speed: Which One Works Faster?
Speed can make or break your workflow. If you’re cutting thick metal and need to move fast, plasma might be your best bet.
- Plasma Cutting: Faster on thicker materials (½ inch and up). For heavy-duty fabrication, repair shops, and metal construction, plasma can cut through steel in seconds.
- Laser Cutting: Faster on thin materials (⅛ inch and below). It can quickly process sheet metal, aluminum, and intricate designs with high accuracy. Blue Elephant laser cutters ensure clean, detailed cuts with minimal material waste.
Precision: How Clean Is The Cut?
Speed is one thing, but what about accuracy? A fast cut isn’t helpful if you’re spending hours cleaning up rough edges.
- Plasma Cutting: Produces wider kerf (cut width) and may leave rough edges, requiring post-processing like grinding.
- Laser Cutting: Delivers razor-sharp precision with a narrow kerf, reducing the need for extra finishing.
When I needed highly detailed, intricate cuts, plasma just didn’t cut it—literally. The edges weren’t as sharp, and I had to spend extra time cleaning them up. But when I needed to slice through thick steel fast, plasma was my go-to.

3. Cost Analysis: Which is More Cost-Effective?
Buying a cutting machine is a big investment. But the upfront price isn’t the only thing that matters—you also need to think about operating costs, maintenance, and long-term value.
So, which one gives you the best return on investment? Let’s break it down.
The first thing most buyers look at is the initial price tag. Here’s how plasma and laser cutters compare:
- Plasma Cutters: Entry-level models start around $2,000–$5,000, while high-end CNC plasma cutters can cost $20,000 or more.
- Laser Cutters: Fiber laser machines start at $15,000–$50,000, and industrial CO₂ lasers can go well beyond $100,000.
If budget is a concern, plasma is the cheaper option. But higher cost doesn’t always mean worse value. Let’s look at long-term expenses.
Operating Costs
Owning the machine is one thing—keeping it running is another.
- Plasma Cutting: Uses compressed air or oxygen and consumes more electricity. Replacement parts like electrodes and nozzles wear out over time.
- Laser Cutting: Uses oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air, but fiber lasers are more energy-efficient than plasma. The main cost comes from laser source replacement, which can be pricey.
Plasma cutters burn through consumables faster. If you’re running high-volume production, these costs add up. Laser cutters, while expensive upfront, tend to have lower daily running costs in the long run.
Labor And Finishing Costs
How much time (and money) do you spend cleaning up cuts?
- Plasma Cutting: Produces rougher edges that may need grinding and polishing. This adds extra labor costs.
- Laser Cutting: Leaves clean, precise edges, reducing the need for post-processing.
If you need speed and minimal cleanup, a laser cutter could save time (which = money). But if your workflow already includes grinding, plasma might still be the better option.
4. Industry Applications: Which Cutter is Best for Your Business?
Not all cutting jobs are the same. A machine shop cutting thick steel plates has different needs than a manufacturer producing delicate metal components. So which cutter is best for your business?
The right choice depends on what you cut, how often you cut, and the level of precision your work demands.
Where Plasma Cutting Works Best
Plasma cutting is a workhorse. It’s fast, tough, and perfect for cutting thick metal in rugged environments. If you’re working with steel, aluminum, or stainless steel and don’t need ultra-fine details, plasma is a solid choice.
Common Industries That Use Plasma Cutting:
- Metal Fabrication: Great for cutting large metal sheets quickly.
- Automotive Repair & Customization: Used to modify frames, panels, and exhaust systems.
- Construction & Infrastructure: Ideal for cutting structural steel and heavy-duty components.
- Shipbuilding & Marine: Handles thick metal used in ship hulls and offshore platforms.
- Industrial Equipment Manufacturing: Cuts components for heavy machinery and tools.
Where Laser Cutting Works Best
Laser cutting shines in industries that need high precision, fine details, and minimal post-processing. If your business relies on tight tolerances and clean edges, laser cutting is the better fit.
Common Industries That Use Laser Cutting:
- Aerospace & Defense: Cuts complex parts for aircraft, satellites, and military equipment.
- Electronics & Medical Devices: Used for cutting thin metal sheets with extreme accuracy.
- Jewelry & Engraving: Creates intricate designs with smooth, polished edges.
- Signage & Advertising: Cuts letters, logos, and decorative elements in various materials.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Used for cutting precision parts in production lines.
5. Durability and Maintenance: Which Machine Lasts Longer?
A cutting machine is a long-term investment, so you want one that holds up over time. But here’s the real question: Which cutter lasts longer and costs less to maintain—plasma or laser?
The answer isn’t just about build quality. It’s about wear and tear, part replacements, and daily upkeep. Let’s look at how both machines hold up in the long run.
How Long Do These Machines Last?
Both plasma and laser cutters can last for years with proper maintenance. However, their lifespans depend on how often they’re used, what materials they cut, and how well they’re maintained.
- Plasma Cutters: Typically last 5 to 10 years in high-production environments. However, they rely on consumable parts like electrodes and nozzles, which wear out over time.
- Laser Cutters: Can last 10 to 15 years, but laser sources degrade and may need replacing after 20,000 to 50,000 hours of use.
What’s The Maintenance Like?
Machines don’t just run forever—they need care. But which one is easier (and cheaper) to maintain?
Plasma Cutter Maintenance:
- Requires frequent nozzle and electrode replacements.
- Torch parts wear out faster, especially under heavy use.
- Needs regular cleaning of dust, slag, and debris to avoid clogs.
- More forgiving if maintenance is skipped but will see performance drops over time.
Laser Cutter Maintenance:
- Lens and mirrors must be kept clean to maintain precision.
- The laser source (CO₂ or fiber) will eventually need replacement.
- More sensitive to dust and misalignment, requiring regular calibrations.
- Requires filtered air systems to keep optics from contamination.
6. Tips To Consider When Choosing The Right Cutter
Choosing between a plasma cutter and a laser cutter isn’t just about specs—it’s about what works best for your business, your workflow, and your budget. But with so many factors to weigh, how do you make the right choice?
I know some businesses regret their decision because they didn’t think ahead. You don’t want to spend thousands on a machine only to realize it doesn’t fit your needs. So before you commit, here are a few key things to consider.
Tip #1 Cutting Precision
If your work requires highly detailed cuts with minimal post-processing, laser cutting is the better option. It produces sharp, clean edges and maintains accuracy even on intricate designs. Plasma cutting, while fast and powerful, leaves wider kerfs and rougher edges, which may require additional grinding or finishing.
Tip #2 Frequency of Use
The right cutter depends on how often your business needs to cut materials. Plasma cutters are built for high-volume, heavy-duty industrial use and can run for long hours with minimal downtime. Laser cutters, while capable of handling large production runs, require a more controlled environment and regular calibration to maintain precision.
Tip #3 Work Environment Requirements
Plasma cutting produces high levels of noise, sparks, and fumes, which means your shop must have proper ventilation and safety measures in place. Laser cutters require a dust-free, controlled workspace to maintain the integrity of the laser beam and prevent contamination of optical components. Your shop’s layout and available space will play a big role in determining the right fit.
Conclusion
You’ve seen the pros and cons. Plasma cutting is fast and tough. Laser cutting is precise and efficient. Now, it’s your turn to decide.
I remember my own mistake—choosing the wrong cutter set me back time and money. You don’t have to go through that. Pick the machine that supports your business, not the one that looks good on paper.
If you are looking for a trusted CNC machine supplier, at Blue Elephant we offfer high-performance machines at competitive prices, often delivering better durability and stability than competitors in the same price range.
Contact us today—we’ll help you build your business with confidence!












